The Haynes 10425 - Automotive Heating and Air Conditioning Manual, shows you the basic theory of A/C and heating system operation.
This DIY manual covers both R-12 and R-134a A/C systems (as well as converting to an R-134a system), types of automotive A/C systems, service and diagnostic tools, and much more.
Hundreds of sharp black and white photos and illustrations complement the text instructions for ease of use.
You can trust a Haynes manual to be a DIY authority when it comes to troubleshooting, maintaining, servicing, replacing and even recharging your automotive air conditioning system. Same goes with the heating system for your car or truck. You will find step-by-step instructions with helpful photos that make things easy to understand and follow.
Save big and do your own work on your car or truck with this Automotive Heating & Air Conditioning Manual from the Haynes Techbook series.
Book Excerpt: Automotive Heating and Air Conditioning: Maintenance, Troubleshooting, Service, Repair HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING
REPLACE THE RECEIVER-DRIER
- When a major leak (broken hose, loose connections, accident damage, etc. allows ambient air and moisture to enter the system.
- When the system is opened for a lengthy period of time without being capped.
- When the sight glass turns cloudy (the desiccant has broken down and flowing through the system).
- When the expansion valve is replaced (expansion valve malfunctions and usually caused by moisture in the system).
- When the Suction Throttling Valve (STV), Pilot Operated Absolute (POA), Evaporator Pressure Regulator (EPR) or expansion valve is replaced (each of these components usually malfunctions when moisture enters the system).
- When the normally warm or hot outlet lines from the receiver-drier are cool during system operation (excessive moisture build-up near the receiver-drier causes formation of condensation on the hoses, indicating a restriction).
- When too much refrigerant oil (more than 5-ounces) accumulates in the receiver-drier (this indicates that the oil bleed hole is clogged and it usually causes poor system performance).
ACCUMULATOR REPLACEMENT The accumulator, which is connected to the evaporator inlet pipe on General Motors and Ford Motor Company accumulator type systems, performs the same functions as the receiver-drier. If the accumulator malfunctions, it must be replaced. It cannot be serviced. Typical accumulator malfunctions are caused by:The procedure for replacing the accumulator in specific vehicles is included in Haynes Automotive Repair Manuals. However, the following general procedure should enable you to replace the accumulator on a vehicle if you don't have the Haynes manual.
- Leaks.
- A restricted orifice tube or compressor inlet screen.
- An internally corroded evaporator.
- Saturated desiccant (desiccant alone can't be replaced).
- Detach the cable from the negative terminal of the battery.
- Discharge the system (minimizing oil loss as much as possible) as outlined previously.
- Disconnect the accumulator inlet and outlet lines and cap all openings to prevent contamination of the system by dirt or moisture.
NOTE: On some 1981 and later Ford Motor Company vehicles, the suction hose must be disconnected at the compressor because the line is not removable at the accumulator.- If the accumulator has a pressure sensing switch, remove it and transfer to the new accumulator.
Subject: Automotive: A/C and heater repair and service manual procedures. R-12 and R-134a systems. ISBN-10: 1563929139 | ISBN-13: 9781563929137 | Haynes 10425
Below: Automotive Heating & AC manual Sample Page. Copyright Haynes Publishing.
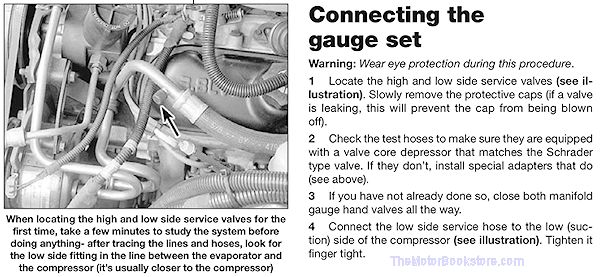
- Preface
- Basic theory of air conditioning system operation
- Basic air conditioning and heating system components
- Typical automotive air conditioning systems
- Service and diagnostic tools
- Heating and air conditioning system service and repair
- Troubleshooting
- Glossary
- Index











